Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Are primates K-selected or R-selected?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chambazone.com in category: Blog sharing the story of making money online. You will find the answer right below.
Examples of K-selected species include birds, larger mammals (such as elephants, horses, and primates), and larger plants.You can see r- and K-selected strategies clearly by looking at different organisms within a phylogenetic group, such as the mammals. For example, elephants are highly K-selected, whereas mice are much more r-selected. Among the fishes, most, like the salmon, are r-selected.K-selection / r-selection: K-selected species reproduce slowly. They produce altricial offspring requiring a long time to maftire. R-selected species reproduce quickly and have many offspring. They produce many precocial offspring that quickly mature. K-selection and r-selection are relative terms.

Are mammals R or K-selected?
You can see r- and K-selected strategies clearly by looking at different organisms within a phylogenetic group, such as the mammals. For example, elephants are highly K-selected, whereas mice are much more r-selected. Among the fishes, most, like the salmon, are r-selected.
What is K selection in primates?
K-selection / r-selection: K-selected species reproduce slowly. They produce altricial offspring requiring a long time to maftire. R-selected species reproduce quickly and have many offspring. They produce many precocial offspring that quickly mature. K-selection and r-selection are relative terms.
K selected and r selected population growth strategies | AP Environmental science | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicK selected and r selected population growth strategies | AP Environmental science | Khan Academy

What are examples of R-selected species?
Examples of r-selected species include pest organisms, such as rodents, insects, and weeds.
Are humans K strategists?
Both across and within species, r and K strategists differ in a suite of correlated characteristics. Humans are the most K of all. K’s supposedly have a longer gestation period, a higher birthweight, a more delayed sexual maturation, a lower sex drive, and a longer life.
Are gorillas K-selected species?
Examples of animals that pursue K strategies are gorillas and whales. The largest of the primates, gorillas require specialized diets (with distinct differences in the diets of mountain and lowland gorillas) and produce a single offspring once every three to four years.
What animals are K strategists?
Organisms whose life history is subject to K-selection are often referred to as K-strategists or K-selected. Organisms with K-selected traits include large organisms such as elephants, humans, and whales, but also smaller long-lived organisms such as Arctic terns, parrots and eagles.
Which organism is most likely to be part of an R-selected species?
R-selected organisms, those emphasizing a fast growth rate, high number of offspring, include rabbits, bacteria, salmon, plants such as weeds and grasses, etc.
See some more details on the topic Are primates K-selected or R-selected? here:
r and K selection
You can see r- and K-selected strategies clearly by looking at different organisms within a phylogenetic group, such as the mammals.
45.3B: Theories of Life History – Biology LibreTexts
K-selection species are defined as those present in stable and predictable environments that produce fewer offspring, have longer gestation …
r/K Selection Theory – Biology | Socratic
How do r selected populations differ from K selected populations? In a nutshell, R selected populations are more “YOLO” type while K selected populations are …
Difference between r and K Selection – Biology Exams 4 U
Wilson (1967). The r selected species live in populations that are highly variable. The fittest individuals in these environments have many offspring and …
Which organisms would be most likely to be K selected?
K selected organisms produce few offspring but invest a lot of energy in them, and examples would include whales, primates (which includes humans), elephants, and some birds, like arctic terns.
What does R mean in apes?
R-Selected Species. weak competitive ability. R-Selected Species. variable population size, often well below carrying capacity. R-Selected Species.
Which of the following is a typical K-selected species adaptation?
Which of the following is a typical K-selected species’ adaptation? K-selected species have a low biotic potential but high survivorship in part because of extended care for their young.
Which example best illustrates a Semelparous K-selected species?
Which example best illustrates a semelparous, K-selected species? Locusts (grasshoppers in the family Acrididae) undergo cyclic population outbreaks, leading to massive swarms.
r and K selection | Ecology
Images related to the topicr and K selection | Ecology

Are bacteria K strategists?
Thus at nearly every point, bacterial cells incorporated into biofilms appear to behave as K-strategists (see figure 4).
Which of the following is an R strategist?
Insects produce a large number of offsprings and fall in the category of r strategist. Thus, the correct answer is B, Insects.
What is an R strategist and K strategist?
The terms r-selection and K-selection are used by ecologists to describe the growth and reproduction strategies of organisms. r-selected species have a high growth rate but low survivability (“cheap” offspring) K-selected species have a low growth rate but high survivability (“expensive” offspring)
Is the western lowland gorilla an R selected or a K-selected species?
a) The Western lowland gorilla is a K-selected species.
What does K selection mean?
📓 High School Level. Ecology. selection occurring when a population is at or near the carrying capacity of the environment, which is usually stable: tends to favor individuals that successfully compete for resources and produce few, slowly developing young, and results in a stable population of long-lived individuals.
What are the characteristics of K-selected species?
K-selected species are characterized by long gestation periods lasting several months, slow maturation (and thus extended parental care), and long life spans. In addition, they tend to inhabit relatively stable biological communities, such as late-successional or climax forests (see ecological succession).
Are turtles R or K-selected?
Similarly, reptiles such as sea turtles display both r- and K-traits: although large organisms with long lifespans (should they reach adulthood), they produce large numbers of unnurtured offspring.
Are pioneer species R or K-selected?
Answer and Explanation: Pioneer species are most commonly R-selected species. This means that they have shorter lifespans, tend to be smaller plants, and usually produce multiple offspring.
Are rabbits R or K strategists?
In r and K selection theory, the rabbit is known as an r-strategist. R-strategists often live in unstable environments, so there’s little chance that their offspring would survive into adulthood.
r and K selection
Images related to the topicr and K selection
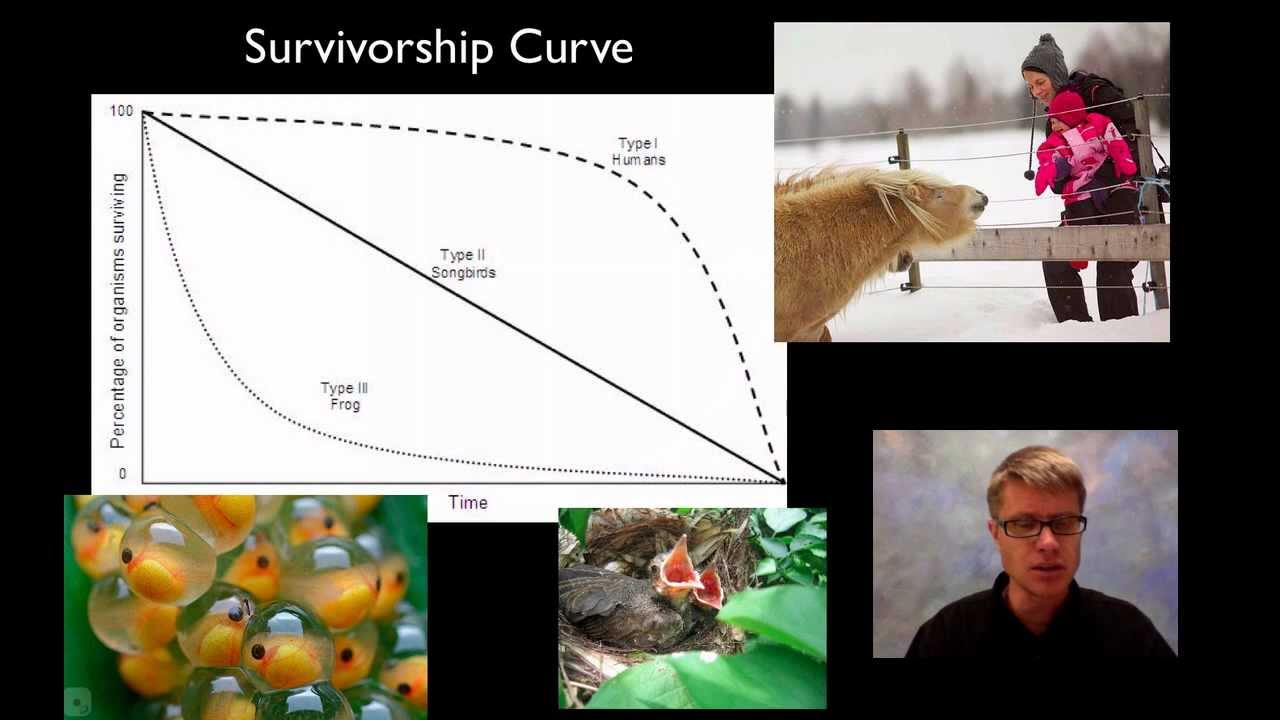
Which of the following is a K strategist?
Species designated as K-strategists thrive through longevity and have a higher survival rate at birth, but produce far fewer offspring. Examples include elephants and whales.
Are cats R or K strategists?
Indeed, one can think of a given organism as an “r-strategist” or a “K-strategist” only relative to some other organism; thus statements about r and K selection are invariably comparative. Cats and dogs are r-selected compared to humans, but K-selected compared to mice and rats.
Related searches to Are primates K-selected or R-selected?
- k selected species
- k-selected species characteristics
- are humans an r-selected or k-selected species
- r and k-selected species
- are primates k-selected or r-selected
- r-selected species
- k selected species characteristics
- r and k selected species
- are primates r selected
- k selected species graph
- r-selected species examples
- what is r selected and k selected
- r selected species examples
- what is r selected and k selected species
- k-selected species
- s selected species
- are squirrels k-selected or r-selected
- j selected species
- what is the difference between r-selected and k-selected species
- r selected species
- ‘s selected species
Information related to the topic Are primates K-selected or R-selected?
Here are the search results of the thread Are primates K-selected or R-selected? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Are primates K-selected or R-selected?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
