Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture) “? We answer all your questions at the website Chambazone.com in category: 40+ Marketing Blog Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
IEEE 802.11 standard, popularly known as WiFi, lays down the architecture and specifications of wireless LANs (WLANs). WiFi or WLAN uses high-frequency radio waves instead of cables for connecting the devices in LAN. Users connected by WLANs can move around within the area of network coverage.WIRELESS LAN- Architecture elements
✓ An 802.11 LAN is based on a cellular architecture where the system is divided. into cells called basic Service set (BSS) and each cell is Controlled by a base station called Access point (AP). ✓ The WLAN can be formed by a single cell or several cells, where the access points.There are several standards of IEEE 802.11 WLANs. The prominent among them are 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11p. All the standards use carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA). Also, they have support for both centralised base station based as well as ad hoc networks.
IEEE 802.11 Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi)
Images related to the topicIEEE 802.11 Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi)
We are nothing more than social animals trying to access the internet for our basic needs (sharing pictures on social media, watching web series, e-commerce, etc.). Most of the time, we use data from our mobile phones or use WiFi to communicate wirelessly. Wireless communication is now becoming the first choice for accessing the Internet (as opposed to wired LAN cables). Therefore, in this article, we will understand the detailed protocol architecture of the wireless LAN standard IEEE 802.11 (WLAN). Another WLAN (Wireless LAN) is Bluetooth (see next article). WiFi is wely used in public places such as offices and universities.
What is wifi (Wireless LAN) ?
IEEE defines a wireless LAN specification called IEEE 802.11, covering both the physical and data link layers. Now let’s look at the different standards and their frequency ranges and supported data rates: The WLAN standard 802.11n uses MIMO antennas (Multiple Input Multiple Output), ie. H. Two or more antennas on the transmit and receive se to transmit/receive different signals. Throughput of over 200 Mbit/s can be achieved using this WLAN standard.
IEEE 802.11 (wifi) Architecture !!
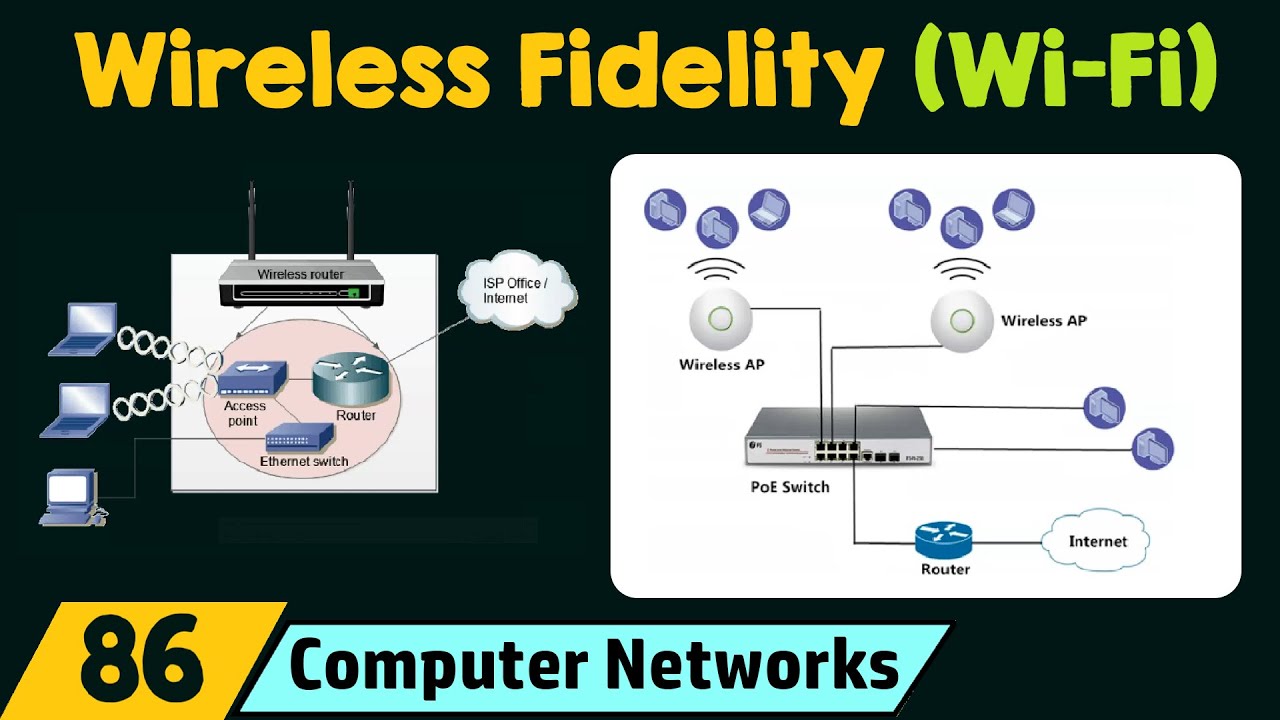
The basic building block of the 802.11 architecture is primarily the Basic Service Set (BSS). A BSS consists of one or more wireless stations and an optional base station called an access point (AP). In a typical home network, there is a wireless router (access point + router) that connects the BSS to the Internet. A BSS without APs is called an ad hoc network. An ad hoc network can form when people using laptops gather in a conference room, train, or car and want to exchange data without a centralized AP. In this mode, the client connects to an access point (AP), which in turn connects to another network, as shown. Clients send and receive their packets through the AP. Many of these APs are connected together to form an extended 802.11 network. A BSS with APs is called an infrastructure network. In this mode, a group of computers can communicate directly with each other without an intermediate access point (AP). In IEEE 802.11, a group of BSSs can be connected through a distributed system (DS) to form an extended service set (ESS). An AP can be entified using a Service Set Identifier (SSID).
IEEE 802.11 (Wifi) Station Types
No Transition Mobile Station: Stationary station or only moving within the BSS. BSS Transition Mobile Station: The station can move from one ESS to another, but IEEE 802.11 does not guarantee that communications will be continuous during this movement. A station is portable if it can be moved from one place to another, but remains stationary during use. The mobile station may move during use.
Active and Passive Scanning for AP
The 802.11 standard requires APs to periodically broadcast beacon frames, each of which contains the AP’s SSID and MAC address. The host selects one of the APs to associate with. This is called passive scanning. In an active scan, the host sends a probe frame, which is received by all APs within range of the wireless host. Let’s understand the main steps involved: Examine the request frame (broadcast) from the host. Check the response frame sent by the AP Association request frame (host to selected AP). Association Response Frame (Selected AP to Host).
IEEE 802.11 Reference Model (protocol architecture)
The following is a high-level diagram of the complete IEEE 802.11 architecture (WLAN model): Distributed Coordination Function One of the two protocols defined by the IEEE at the MAC sublayer is called the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF). DCF uses CSMA/CA as the access method (described in the previous article). Before sending a frame, the source station obtains the medium by checking the energy level of the carrier frequency. Point Coordination Function (PCF) PCF is an optional access method that can be implemented in an infrastructure network (rather than an ad hoc network). PCF has a centralized uncontended round-robin access method. The AP polls the stations that can be polled. The polling process is performed by the point coordinator (PC) in the AP within the ESS. PCF is implemented on top of DCF and is mainly used for time-sensitive transmissions.
IEEE 802.11 (wifi) Frame Format
First, let’s decode the fields it contains: FC: The FC field is 2 bytes long and defines the frame type and some control information. D: In all frame types except one, this field usually defines the duration of the transmission. Address: There are four address fields, each 6 bytes long. Sequence Control: This field defines the sequence number of the frame to be used in flow control. Frame Body: This field ranges from 0 to 2312 bytes and contains type-based information. FCS: The FCS field is 4 bytes long and contains a CRC-32 error detection sequence. IEEE 802.11 supports 3 types of frames: management frames, control frames and data frames. Management frames are used for the initial communication between the station and the AP. It is used for site-to-AP association and disassociation, timing and synchronization, and authentication methods. Control frames are used for access channels and acknowledgement frames. Data frames are used for data transfer.
Addressing Mechanism in IEEE 802.11 (Wifi) protocol
The IEEE 802.11 addressing mechanism basically specifies four cases, defined by the values of two flags in the FC field. Address 1 is always the address of the next device. Then address 2 is always the address of the previous device. If address 1 is undefined, address 3 is the address of the final destination station (host). Address 4 is the address of the original source station, which is different from address 2.
Different specifications of IEEE 802.11 (wifi WLAN)
Now let’s understand the other specifications of the IEEE 802.11 reference model: 1. IEEE 802.11a IEEE 802.11a OFDM explains Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for signal generation in the 5 GHz ISM band. Sources compete with each other for access at the data link layer. The frequency band is dived into 52 subbands, of which 48 subbands are used for simultaneous transmission of 48 bit groups and 4 subbands are used for control information. OFDM uses PSK and QAM for modulation. 2. IEEE 802.11b IEEE 802.11b DSSS describes a high-speed direct-sequence spread spectrum (HR-DSSS) technique for signal generation in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. HR-DSSS is entical to DSSS, except for a coding technique called Complementary Keying (CCK). CCK encodes 4 or 8 bits into the CCK symbol. 3. IEEE 802.11g This new specification simply defines forward error correction and OFDM using the 2.4 GHz ISM band. The modulation process achieves data rates of 22 or 54 Mbit/s. It is backward compatible with 802.11b, but the modulation technique is OFDM. In the next article, we’ll dive into the next wely used type of WiFi, the Bluetooth capability. So stay tuned. report this ad
What is wireless LAN architecture?
WIRELESS LAN- Architecture elements
✓ An 802.11 LAN is based on a cellular architecture where the system is divided. into cells called basic Service set (BSS) and each cell is Controlled by a base station called Access point (AP). ✓ The WLAN can be formed by a single cell or several cells, where the access points.
What are the IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standards?
There are several standards of IEEE 802.11 WLANs. The prominent among them are 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11p. All the standards use carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA). Also, they have support for both centralised base station based as well as ad hoc networks.
Is IEEE 802.11 and WiFi same?
The technical name for WiFi is IEEE 802.11 & and it provides wireless communications within a wireless local area network, often to an access point or wireless router / hotspot. Wi-Fi wireless connectivity is an established part of everyday life.
How does WiFi 802.11 work?
802.11b transmits in the 2.4 GHz frequency band of the radio spectrum. It can handle up to 11 megabits of data per second, and it uses complementary code keying (CCK) modulation to improve speeds. 802.11a (introduced after 802.11b) transmits at 5 GHz and can move up to 54 megabits of data per second.
What are 3 types of wireless connections?
There are basically three different types of wireless networks – WAN, LAN and PAN: Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN): WWANs are created through the use of mobile phone signals typically provided and maintained by specific mobile phone (cellular) service providers.
Why wireless LAN are used?
Wireless LANs provide high speed data communication in small areas such as building or an office. WLANs allow users to move around in a confined area while they are still connected to the network.
What are two characteristics of 802.11 wireless networks?
- Stations can transmit at any time.
- They use CSMA/CA technology.
- They are collision-free networks.
- They use CSMA/CD technology.
- Collisions can exist in the networks.
What is the best Wi-Fi standard?
| Standard | Released | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 5/IEEE 802.11ac | 2013 | 450 Mbps/1300 Mbps |
| IEEE 802.11ad (WiGig) | 2012 | 6.7 Gbps |
| IEEE 802.11ah (HaLow) | 2016 | 347 Mbps |
| Wi-Fi 6/IEEE 802.11ax | 2019 est. | 450 Mbps/10.53 Gbps |
Where is IEEE 802.11 used?
IEEE 802.11 Architecture
Clients are workstations, computers, laptops, printers, smartphones, etc.
What does Wi-Fi mean?
Wi-Fi, often referred to as WiFi, wifi, wi-fi or wi fi, is often thought to be short for Wireless Fidelity but there is no such thing. The term was created by a marketing firm because the wireless industry was looking for a user-friendly name to refer to some not so user-friendly technology known as IEEE 802.11.
What is the frequency range of IEEE 802.11 a standard?
Operates in the 5 GHz frequency range (5.125 to 5.85 GHz) with a maximum 54 Mbps signaling rate.
See some more details on the topic What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture) here:
Wireless LAN and IEEE 802.11 – Tutorialspoint
Wireless LANs are those Local Area Networks that use high frequency radio waves instead of cables for connecting the devices in LAN.
Wireless LAN -Architecture – CourSys
✓IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers.
IEEE 802.11 – Wikipedia
IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, … the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the …
What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture) ?
So in this post, we will understand the in-depth protocol architecture of IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard (wifi). The other WLAN (wireless …
Related searches to What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture)
- wifi 802 11 bgn la gi
- ieee 802 11 la gi
- what is wireless wlan
- IEEE 802.11 standards
- ieee 802 11 standards
- ieee 802.11 b/g/n
- Ieee 802.11 là gì
- what is wireless standard
- what is wifi 802.11ac
- 802.11 frame
- wifi 802.11 b/g/n là gì
- 802 11 frame
- what is wireless 802.11
- what is wireless lan 802.11
- wireless frame structure
- Wireless frame structure
- ieee 802 11 bgn
- what is wifi 802.11
Information related to the topic What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture)
Here are the search results of the thread What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture) from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is Wifi (IEEE 802.11 Wireless Lan Architecture) . If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
