Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model“? We answer all your questions at the website Chambazone.com in category: 40+ Marketing Blog Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
TCP/IP Reference Model is a four-layered suite of communication protocols. It was developed by the DoD (Department of Defence) in the 1960s. It is named after the two main protocols that are used in the model, namely, TCP and IP. TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and IP stands for Internet Protocol.TCP/IP specifies how data is exchanged over the internet by providing end-to-end communications that identify how it should be broken into packets, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.TCP/IP relies on the transport layer to effectively control communications between two hosts. When an IP communication session must begin or end, the transport layer is used to build this connection.
| OSI Ref. Layer No. | OSI Layer Equivalent | TCP/IP Protocol Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Transport | TCP, UDP |
| 3 | Network | IP, ARP, ICMP |
| 2 | Data link | PPP, IEEE 802.2 |
| 1 | Physical | Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) Token Ring, RS-232, others |
Table of Contents
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite
Images related to the topicThe TCP/IP Protocol Suite
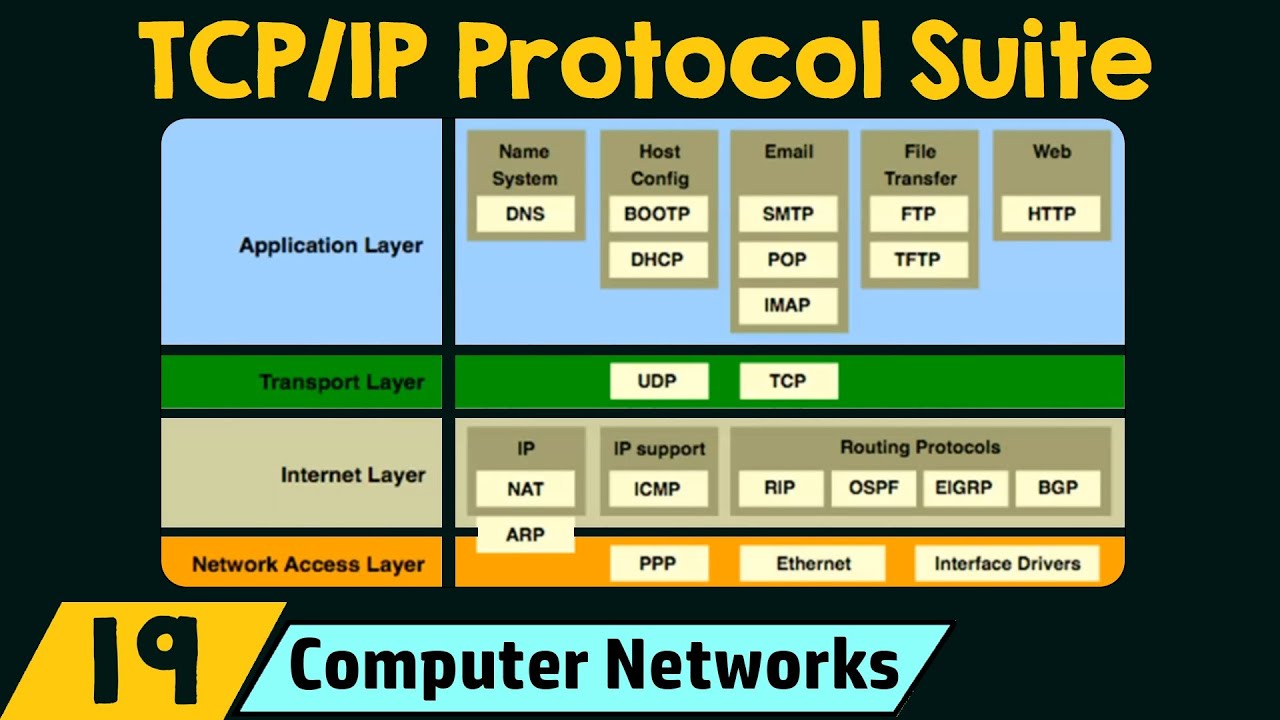
In the previous article, we saw a complete overview of the OSI reference model and all its different layers. Now we see the next important reference model, the TCP/IP reference model. This is an acronym for Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. This is another reference model formerly used by ARPANET (a research network sponsored by the US Department of Defense), now used on the Internet. If we simply compare the two reference models, we can say that the host to network layer corresponds to a combination of physical and data link layers, while the internet layer corresponds to the network layer. The application layer roughly handles the tasks of the session layer, presentation layer, and application layer, while the transport layer in TCP/IP takes over some of the responsibilities of the session layer. Currently, existing protocols cannot handle the integration of satellite networks. Therefore a new reference architecture is required. Due to the use of both the TCP and IP protocols, the new architecture is called the TCP/IP Reference Model.
Introduction to TCP/IP
TCP/IP is a layered protocol, and the term layered means that each higher-level protocol is supported by one or more lower-level protocols. Like any other communication protocol, the Internet Protocol is a set of rules that govern all possible communications on the Internet. These two protocols (TCP and IP) describe the movement of data between hosts on the Internet. At the transport layer, TCP/IP defines three protocols, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) (all of these indivual protocols will be discussed in subsequent articles). In addition, at the network layer, the main protocol defined by TCP/IP is the Internetworking Protocol (IP). There are different layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite, each responsible for a different type of communication. TCP/IP proves a simple naming and addressing scheme that makes it easy to find various resources on the Internet. Information on the Internet is transmitted in “packets”. The IP protocol is used to package messages into “packets”. Each package contains the sender’s address and the recipient’s address. These addresses are called IP addresses. Using the TCP protocol, a single large message is broken up into a series of packets, each of which is packaged into an IP packet. Packets are passed from one network to another until they reach their destination. At the destination, the TCP software reassembles the packets into a complete message. All packets in a single message do not have to take the same route each time they are sent. TCP/IP Model Architecture Overview Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) were developed by the Defense Program Research Agency (ARPA, later DARPA) as part of its Network Interconnection program. TCP/IP is the most wely used protocol for connecting computers and is the protocol of the Internet. OSI Model TCP/IP Model Application Application Demonstration TCP/IP Session Transport Transport Network Internet Data Connection Host to Physical Network These two layers are missing With the development of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Hypertext Markup Language can be freely exchanged (HTML) document. The Internet, the World We Web (WWW), was born, and soon TCP/IP was wely used. In the figure you can see the TCP/IP reference model and the OSI model for comparison.
Description of TCP/IP Model:
Internet Layer :
This layer, called the internet layer (or internetwork layer), holds the entire architecture together. The job of this layer is to allow the host to insert packets into any network and then have them reach their destination independently. It uses four supporting protocols: ARP, RARP, ICMP, and IGMP (all of these protocols will be explained in more detail in later articles). Internet Protocol (IP) is an unreliable and connectionless protocol delivery service. IP does not prove error checking or tracing. It assumes underlying unreliability and does its best to deliver the transmission to its destination, but proves no service guarantees. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to map logical addresses to physical addresses (using network interface cards). Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) allows any host to discover its Internet address given only its physical address. The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is the mechanism that hosts and gateways use to send notifications of datagram problems back to the sender. The Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) is used to facilitate the simultaneous transmission of messages to a group of recipients. The order in which packets are received may not be the same as the order in which they were sent. The Internet layer defines (specifies) the packet format and protocol known as the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, packet routing and congestion control are important issues associated with this layer. The TCP/IP internet layer is very similar to the network layer in the OSI model shown above.
Transport Layer :
This layer allows peer entities of the source and target machines to communicate with each other. The end-to-end protocols used here are TCP and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP is a reliable connection-oriented protocol. It allows a stream of bytes transferred from one machine to another without introducing any errors. TCP is a reliable streaming protocol. In this context, the term stream means connection-oriented. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the second protocol used in the transport layer. UDP and TCP are transport layer protocols responsible for passing messages from one process (executed program) to another. It is an unreliable connectionless protocol for applications that do not require TCP ordering or flow control. UDP is a process-to-process protocol that only adds port addresses, checksum error checking and length information to the upper layer data. UDP also outperforms TCP in applications where immediate delivery is more important than accurate delivery of voice or video transmissions.
Application Layer:
The TCP/IP model has no session or presentation layers, as they are not important in most applications. The application layer in TCP/IP corresponds to the combination of session layer, presentation layer and application layer in the OSI model. The protocols associated with this layer are high-level protocols such as B. Virtual Terminal (TELNET), File Transfer (FTP), and Email (SMTP) (all of which will be covered in later articles). Many other protocols have been added over the years, such as: B. Domain Name Service (DNS), NNTP, HTTP, etc.
Host to Network Layer :
This is the lowest layer in the TCP/IP reference model. At the physical and data link layers, TCP/IP does not define any specific protocol. It supports all standard and proprietary protocols. The network in a TCP/IP internetwork can be a local area network or a we area network. A host needs to use a protocol to connect to the network so that it can send IP packets over it. See the table below for a brief summary of the protocols implemented in these layers: Protocols used by the TCP/IP layer Application layer FTP, SMTP, DNS, HTTP, NNTP Transport TCP, UDP Internet/Network IP host to network LAN , Packet Radio In the following articles, we will describe each protocol in detail. In the next article, we will see the different types of addressing that arise in any computer network. So stay tuned. report this ad
What is Transmission Control Protocol Internet Protocol TCP IP reference and how it works?
TCP/IP specifies how data is exchanged over the internet by providing end-to-end communications that identify how it should be broken into packets, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.
What layer in the Transmission Control Protocol Internet Protocol TCP IP model does IP use?
TCP/IP relies on the transport layer to effectively control communications between two hosts. When an IP communication session must begin or end, the transport layer is used to build this connection.
What are the four types of TCP IP reference model?
There are four layers of the TCP/IP model: network access, internet, transport, and application. Used together, these layers are a suite of protocols. The TCP/IP model passes data through these layers in a particular order when a user sends information, and then again in reverse order when the data is received.
What is TCP IP protocol with diagram?
| OSI Ref. Layer No. | OSI Layer Equivalent | TCP/IP Protocol Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Transport | TCP, UDP |
| 3 | Network | IP, ARP, ICMP |
| 2 | Data link | PPP, IEEE 802.2 |
| 1 | Physical | Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) Token Ring, RS-232, others |
What is the main purpose of the Transmission Control Protocol TCP?
TCP is used for organizing data in a way that ensures the secure transmission between the server and client. It guarantees the integrity of data sent over the network, regardless of the amount. For this reason, it is used to transmit data from other higher-level protocols that require all transmitted data to arrive.
How does a TCP connection work?
How exactly do TCP connections work? TCP allows for transmission of information in both directions. This means that computer systems that communicate over TCP can send and receive data at the same time, similar to a telephone conversation. The protocol uses segments (packets) as the basic units of data transmission.
How many layers are in TCP IP model?
4 The TCP/IP Protocol Stack is made up of four primary layers: the Application, Transport, Network, and Link layers (Diagram 1). Each layer within the TCP/IP protocol suite has a specific function. When the layers of the model are combined and transmitted, communication between systems can occur.
What layer in the Transmission Control Protocol Internet Protocol TCP IP model does IP use quizlet?
At which layer of the OSI model does IP addressing take place? At the Network layer (layer 3), the Internet Protocol (IP) provides logical host and network addressing and routing.
What are the 5 layers of TCP IP?
The TCP/IP model is based on a five-layer model for networking. From bottom (the link) to top (the user application), these are the physical, data link, net- work, transport, and application layers.
How many protocols are in TCP IP?
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and the Router Discovery Protocol (RDISC) are two routing protocols for TCP/IP networks.
What is a reference model in computer network?
In computer networks, reference models give a conceptual framework that standardizes communication between heterogeneous networks. The two popular reference models are − OSI Model. TCP/IP Protocol Suite.
See some more details on the topic Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model here:
What is TCP/IP and How Does it Work? – TechTarget
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol and is a suite of communication protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet …
TCP/IP Model – GeeksforGeeks
It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The TCP/IP model is a concise version of the OSI model.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol – IBM
TCP/IP is a suite of protocols that specify communications standards between computers and detail conventions for routing and interconnecting networks. It is …
What is Transmission Control Protocol TCP/IP Model? – Fortinet
The TCP/IP model is the default method of data communication on the Internet. It was developed by the United States Department of Defense to enable the accurate …
Related searches to Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model
- tcp ip network
- tcpip stands for la gi
- tcp ip reference model
- tcpip protocol suite
- List some protocols TCP/IP HTTP DNS ICMP
- tcp/ip stands for là gì
- list some protocols tcpip http dns icmp
- tcp/ip stands for
- TCP/IP protocol suite
- the tcpip model has
- advantages and disadvantages of tcp ip model
- TCP IP Reference Model
- tcpip stands for
- The TCP/IP model has
Information related to the topic Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model
Here are the search results of the thread Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Transmission Control ProtocolInternet Protocol (TCPIP) Reference Model. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
