Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chambazone.com in category: Blog sharing the story of making money online. You will find the answer right below.
Small antifreeze proteins (less than 150 residues) are often represented by structures with hydrophobic core.Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) are specific proteins, glycopeptides, and peptides made by different organisms to allow cells to survive in sub-zero conditions. AFPs function by reducing the water’s freezing point and avoiding ice crystals’ growth in the frozen stage.Unusually, AFPs have many hydrophobic amino acids on their surface. These form part of the special binding surface that only sticks to ice nuclei, ie to solid but not liquid H2O.

What type of proteins are antifreeze?
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) are specific proteins, glycopeptides, and peptides made by different organisms to allow cells to survive in sub-zero conditions. AFPs function by reducing the water’s freezing point and avoiding ice crystals’ growth in the frozen stage.
Are Arctic fish antifreeze proteins hydrophobic?
Unusually, AFPs have many hydrophobic amino acids on their surface. These form part of the special binding surface that only sticks to ice nuclei, ie to solid but not liquid H2O.
All About Antifreeze Proteins
Images related to the topicAll About Antifreeze Proteins

What is the role of antifreeze protein?
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) protect certain cold-adapted organisms from freezing to death by selectively adsorbing to internal ice crystals and inhibiting ice propagation.
Are antifreeze proteins glycoproteins?
Antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) constitute the major fraction of protein in the blood serum of Antarctic notothenioids and Arctic cod.
What are antifreeze glycoproteins?
Antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) are a novel class of biologically significant compounds that possess the ability to inhibit the growth of ice both in vitro and in vivo. Any organic compound that possesses the ability to inhibit the growth of ice has many potential medical, industrial, and commercial applications.
What is the structure of antifreeze?
Antifreeze Proteins (PDB entry 2pne)
In the crystal structure, the ice-binding surface of the protein is covered with strings of water molecules (shown here in red). These water molecules are spaced similarly to the water molecules in ice crystals.
How do antifreeze proteins keep fish from freezing?
The antifreeze molecules allow icefish to live in subfreezing water by plugging gaps in existing small ice crystals and preventing the attachment of more ice molecules. Ice crystal growth is thus effectively stopped. To survive, Antarctic fishes have developed proteins that act as antifreeze.
See some more details on the topic Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic? here:
Antifreeze protein hydration waters – PNAS
Thus, both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups seem to be important in conferring AFPs with an affinity for ice.
Why do antifreeze proteins require a solenoid? – ScienceDirect
Structure of hydrophobic core influences the water structuralization. Universal model of antifreeze action is independent on the protein structure.
Neutron science explains mystery of how Arctic fish’s …
Biological proteins usually have hydrophobic amino acids in the core (away from water molecules in the solvent) and hydrophilic amino acids …
How antifreeze proteins bind to surface of ice crystals
The ice binding surface of an AFP contains both hydrophobic or ‘water repelling’ groups as well as hydrophilic or ‘water loving’ groups.
How do antifreeze proteins keep fish from freezing what would happen if you placed a fish without antifreeze proteins into Antarctic waters?
As the antifreeze proteins circulate through the blood, they bind to ice crystals and prevent them from growing. The fish’s blood thus does not freeze and continues to flow normally. As other species of fish died off in Antarctic waters, this adaptation allowed notothenioids to thrive and diversify.
Which fish have antifreeze proteins?
These “antifreeze proteins”, as they are commonly known, bind to tiny ice crystals in their bodies, inhibiting further growth. To survive the frigid waters of the Arctic Ocean, the Arctic cod—a genetically unrelated fish to the Notothenioids—developed an antifreeze protein nearly identical to the Notothenioid one.
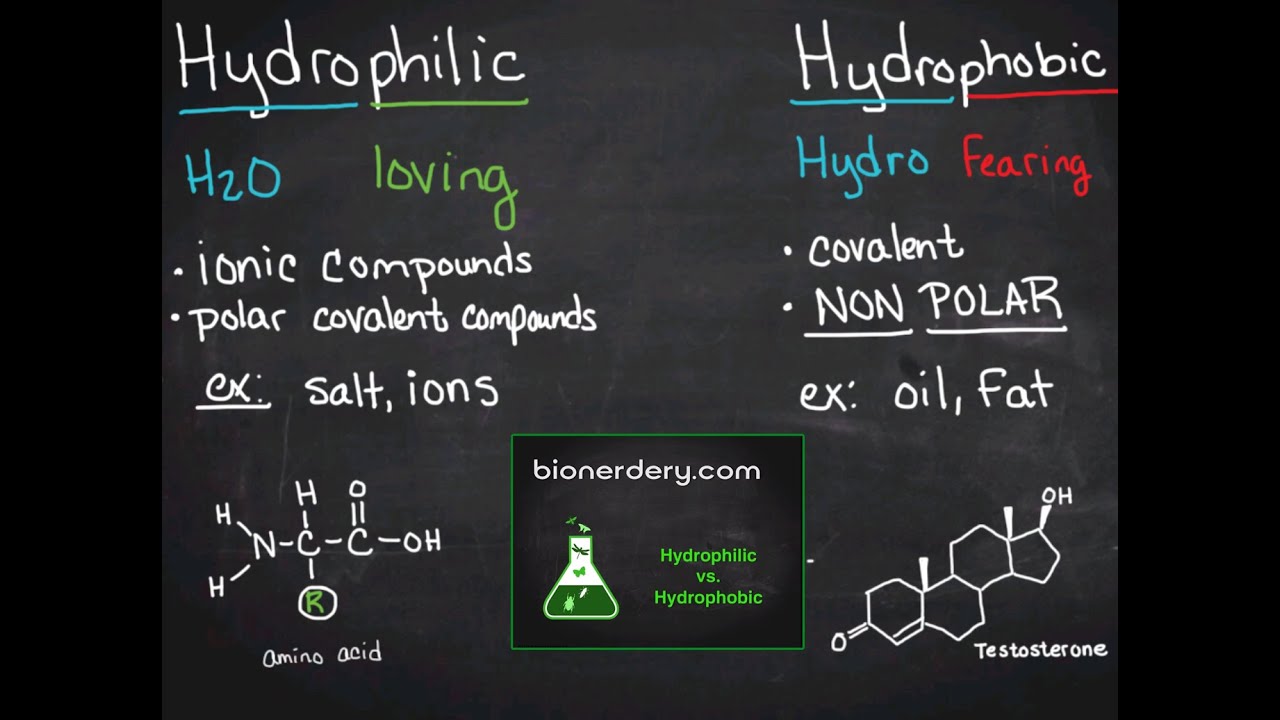
Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic
Images related to the topicHydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic
What is antifreeze membrane made of?
The composition is a Non-Toxic material made from: Fiber, Temperature Inhibitors, Essence, Solubilizer, Water, Cellulose Hydroxyl, and Polyethylene Glycol The Antifreeze Membrane can handle temperatures from -25C to 15C to reduce freeze burns.
Where do antifreeze proteins come from?
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) are biological antifreeze materials originally found in polar fish; AFPs can bind to ice and subsequently inhibit the growth of the ice crystals. Fish can inhabit ice-laden or cold seawater below the freezing point (−0.7 °C) of their blood serum by virtue of AFPs [1,2,3,4].
Why do Antarctic fish have antifreeze proteins in their blood?
In the icy waters of the Antarctic, most of the native fish have special proteins in their blood that act like antifreeze. The proteins bind to ice crystals, keeping them small to prevent the formation of fish popsicles.
What plants have antifreeze proteins?
Secreted PR proteins with antifreeze activity have now been isolated from winter rye, bittersweet nightshade (Solanum dulcamara) and carrot, and include b-1,3-glucanases, chitinases, thaumatin-like proteins [20,21], and a polygalacturonase inhibitor protein [22,23].
Do mammals have antifreeze proteins?
…
Antifreeze protein.
| Insect antifreeze protein, Tenebrio-type | |
|---|---|
| InterPro | IPR003460 |
| SCOP2 | 1ezg / SCOPe / SUPFAM |
Which of the following anti freeze materials are added to the water for the ease of cold starting?
Mass of ethylene glycol which should be added to 4 kg of water to prevent it from freezing at −6oC will be (Kf for water =1.
How can a fish in the Arctic keep its cell membranes from freezing solid?
Fish living in cold climates have evolved an adaptation to keep from freezing: antifreeze proteins. Arctic and Antarctic fish families have these proteins in their blood. They’re part of why these fish can live in waters that other fish can’t.
Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic | Substances | Cell Membranes
Images related to the topicHydrophilic vs Hydrophobic | Substances | Cell Membranes

How did the ice fish get the antifreeze gene?
The researchers show that the gene for antifreeze glycoprotein (AFGP), found in the Antarctic family of notothenioid fishes, evolved in a unique way: arising “whole cloth” from trypsinogen, an enzyme produced by the pancreas. New genes are usually created through recycling of existing protein genes.
When did the antifreeze protein evolve?
The discovery of antifreeze proteins began in the early 70s when Arthur DeVries reported a distinct glycoprotein in Antarctic fish’s blood serum, which helped them to survive at −0.7°C (Chen et al., 1997; Fletcher et al., 2001).
Related searches to Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
- are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic quizlet
- are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic hydro
- is water hydrophobic or hydrophilic
- are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic spray
- are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic molecules
- are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic hydroph
Information related to the topic Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Here are the search results of the thread Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Are antifreeze proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
