Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Are potassium channels open at resting potential?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chambazone.com in category: Blog sharing the story of making money online. You will find the answer right below.
The inside of the cell and the outside of the cell are separated by a membrane with potassium channels, which are initially closed. There is a higher concentration of potassium ions on the inside of the cell than on the outside.At normal resting membrane potential, sodium is forced outwards and potassium is carry into the cells (see Fig. 2.4). This requires the sodium-potassium exchange pump, which uses ATP in order to operate. Three intracellular sodium ions will be exchanged for every two extracellular potassium ions.Permeability at Rest
Significantly more potassium channels are open than sodium channels, and this makes the membrane at rest more permeable to potassium than sodium.
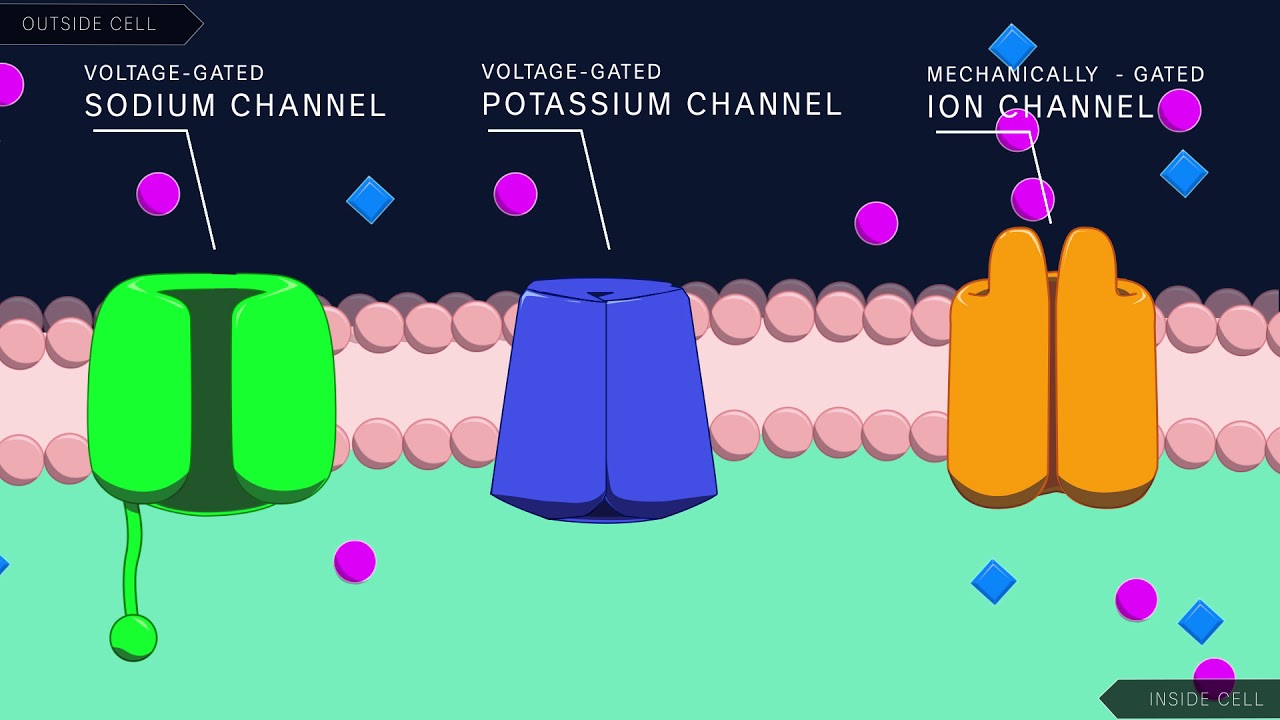
What happens to potassium at resting potential?
At normal resting membrane potential, sodium is forced outwards and potassium is carry into the cells (see Fig. 2.4). This requires the sodium-potassium exchange pump, which uses ATP in order to operate. Three intracellular sodium ions will be exchanged for every two extracellular potassium ions.
Are K+ channels open at rest?
Permeability at Rest
Significantly more potassium channels are open than sodium channels, and this makes the membrane at rest more permeable to potassium than sodium.
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron

Are potassium leak channels always open?
Sodium leak channels further enhancing the influx of sodium ions, while potassium leak channels allow potassium ions to diffuse out of the cell. It doesn’t matter if the neuron is at the resting membrane potential, depolarizing, repolarizing, or hyperpolarizing; the leak channels are always open.
At what potential do potassium channels open?
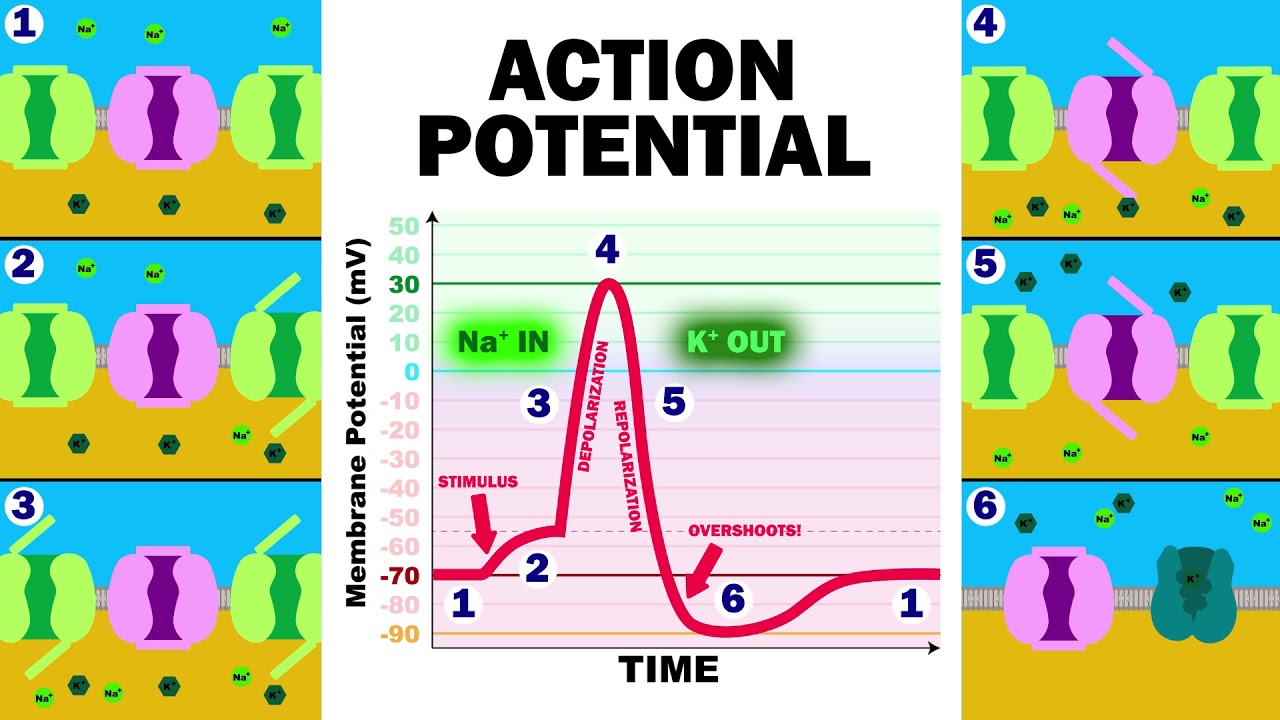
Potassium channels are also stimulated by depolarization, but open about one millisecond later and are responsible for the repolarizing phase of the action potential. Potassium channels open just as the sodium channels are closing.
Do potassium channels close during depolarization?
After a cell has been depolarized, it undergoes one final change in internal charge. Following depolarization, the voltage-gated sodium ion channels that had been open while the cell was undergoing depolarization close again. The increased positive charge within the cell now causes the potassium channels to open.
What happens at resting potential?
resting potential, the imbalance of electrical charge that exists between the interior of electrically excitable neurons (nerve cells) and their surroundings.
Are potassium channels open during hyperpolarization?
Hyperpolarization is a phase where some potassium channels remain open and sodium channels reset. A period of increased potassium permeability results in excessive potassium efflux before the potassium channels close.
See some more details on the topic Are potassium channels open at resting potential? here:
Physiology, Resting Potential – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
The membrane is permeable to K+ at rest because many channels are open. In a normal cell, Na+ permeability is about 5% of the K+ permeability or …
Resting Membrane Potential | Biology for Majors II – Lumen …
Some ion channels need to be activated in order to open and allow ions to pass into or out of the cell. These ion channels are sensitive to the environment and …
Resting Potential – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
At resting membrane potential, ions move through leak channels, which are membrane channels that stay open. Some ions are moved in or out of cells by active …
Resting potential – Wikipedia
The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from …
What causes voltage-gated K+ channels to open?
Voltage-gated potassium channels (KV) are a large group of channels supporting K+ efflux when they open in response to membrane depolarization.
Which statement about resting potential is true?
The only correct statement about the resting membrane potential is c) The resting membrane potential for most animal cells is negative because the inside of the cell is more negatively charged than the outside of the cell.
What channels are always open?
Passive channels, also called leakage channels, are always open and ions pass through them continuously.
Are gated channels always open?
The second important distinction between ion channels and simple aqueous pores is that ion channels are not continuously open. Instead, they are gated, which allows them to open briefly and then close again (Figure 11-20). In most cases, the gate opens in response to a specific stimulus.
How do leak channels maintain resting membrane potential?
What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.
THE ACTION POTENTIAL
Images related to the topicTHE ACTION POTENTIAL
Are sodium channels open at rest?
Typically, sodium channels are in a resting or “closed” state in neurons or muscle cells that are at rest (with a membrane potential of approximately −60 to −80 mV). Closed sodium channels do not conduct sodium ions, but are ready to be activated or “opened” when stimulated by membrane depolarization.
When a neuron is at its resting potential?
The resting membrane potential of a neuron is about -70 mV (mV=millivolt) – this means that the inside of the neuron is 70 mV less than the outside. At rest, there are relatively more sodium ions outside the neuron and more potassium ions inside that neuron.
Are potassium channels open during absolute refractory period?
This is considered the absolute refractory period. The voltage-gated potassium channels are slower to open than the voltage-gated sodium channels. By the time the sodium overshoot has peaked, the voltage-gated potassium channels are open, allowing an efflux of potassium out of the cell.
What channels are open during depolarization?
During the depolarization phase, the gated sodium ion channels on the neuron’s membrane suddenly open and allow sodium ions (Na+) present outside the membrane to rush into the cell. As the sodium ions quickly enter the cell, the internal charge of the nerve changes from -70 mV to -55 mV.
Why do potassium channels open slowly?
As noted above, the voltage-gated K+ channels close slowly after the membrane has been repolarized. Consequently, the K+ conductance is higher (and the neuronal membrane is more hyperpolarized) at the end of the action than in the normal resting state.
What channel opens in response to membrane depolarization?
When the presynaptic membrane is depolarized, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and allow Ca2+ to enter the cell.
Why is the resting membrane potential not equal to the potassium equilibrium potential?
The resting potential is -60 mV. Note that the resting potential is not equal to the K+ equilibrium potential because, as discussed previously, there is a small resting Na+ permeability that makes the cell slightly more positive than EK.
How is the resting potential maintained?
Resting membrane potentials are maintained by two different types of ion channels: the sodium-potassium pump and the sodium and potassium leak channels. Firstly, there is a higher concentration of thepotassium ions inside the cell in comparison to the outside of the cell.
Which of the following shows the resting potential?
6. Which of the following shows resting potential? Explanation: Body cell which showing resting potential is known as a polarised cell.
What is the resting membrane potential of hyperpolarization?
After hyperpolarization the potassium channels close and the natural permeability of the neuron to sodium and potassium allows the neuron to return to its resting potential of –70 mV.
Resting membrane potential – definition, examples
Images related to the topicResting membrane potential – definition, examples
What happens to potassium during repolarization?
The repolarization phase usually returns the membrane potential back to the resting membrane potential. The efflux of potassium (K+) ions results in the falling phase of an action potential. The ions pass through the selectivity filter of the K+ channel pore.
What happens when potassium channels open?
A set of voltage-gated potassium channels open, allowing potassium to rush out of the cell down its electrochemical gradient. These events rapidly decrease the membrane potential, bringing it back towards its normal resting state.
Related searches to Are potassium channels open at resting potential?
- graded potential la gi
- resting membrane potential
- Resting potential
- relationship between resting potential and action potential
- at resting membrane potential voltage-gated potassium ion channels are open
- action potential
- are potassium channels open at resting potential
- equilibrium potential
- are potassium channels always open
- resting potential
- Graded potential là gì
- Action potential
- are voltage gated channels open or closed at resting potential
- what happens to membrane potential when potassium channels open
- what is membrane potential
- What is membrane potential
- sodium channels close and potassium channels open
- the equation of membrane potential
- Equilibrium potential
- Resting membrane potential
- what happens when voltage-gated k+ channels open
Information related to the topic Are potassium channels open at resting potential?
Here are the search results of the thread Are potassium channels open at resting potential? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Are potassium channels open at resting potential?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
